Abstract
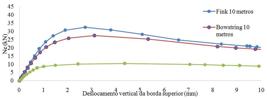
The NBR 7190 (ABNT, 1997) assumes the mean value of the elasticity module to compression in the direction parallel to grain (E c0,m ) as being the representative for all roof structure bars. Due to the variability of woods, such methodology can result in displacement values higher than the limit defined by the standard, which can generate pathologies in the structure. In order to evaluate the influence of the use of E c0,m on the displacement calculation, experimental tests were carried out to obtain the mechanical properties of the wood species Sebastianiacommersoniana (Baillon) Smith & Downs. With the aid of numerical simulations and experimental values, three typologies (fink, bowstring and parallel chord) and two spans (10 m and 20 m) were analysed. Adopting E c0,m , the maximum loads for a displacement of L/200 were determined. After, random stiffness values were assigned to each element of the truss, measuring the maximum displacement of each model. In models where the modulus of elasticity was randomly assigned, superior arrows were observed in approximately 28% and 32% for spans of 10 m and 20 m, respectively. It may explain some pathologies that can be avoided with non-destructive pre-classification and the rational placement of parts in the most vulnerable areas.
Keywords:
FEM; Compression parallel to grain; Stiffness; Truss; Nonlinearanalysis

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail




 Nota: Legenda: /
Nota: Legenda: /
 Fonte:
Fonte:  Fonte:
Fonte: 
