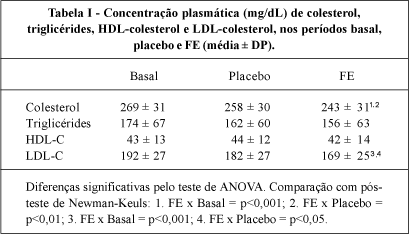
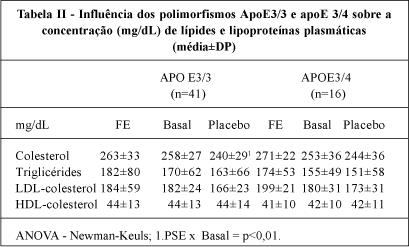
OBJECTIVE - This study aimed at relating the pattern of response to dietary plant sterol ester (PSE) treatment of plasma lipids concentrations and apo E polymorphisms. METHODS - Patients (20-60y old: 50 women; 10 men) with primary moderate hypercholesterolemia were fed margarine (20g/d), received no treatment (placebo), and were fed PSE (2.8g/d = 1.68 phytosterols), during 3 periods of 4 weeks each, in a crossover, double-blind study. DNA was extracted from white blood cells for the apo E polymorphisms. RESULTS - PSE treatment significantly lowered TC and LDL-C 10% and 12%, respectively, in relation to the baseline, and 6% and 8% in relation to the placebo phase, but HDL-C and TG levels were not modified. In regard to the apo E genotyping, no significant difference occurred between apo E 3/3 and apo E 3/4. CONCLUSION - Dietary plant sterol ester (PSE) treatment reduced cholesterolemia, and the reduction of LDL-C in absolute values was more pronounced when the initial LDL - C concentration were elevated.
plant sterol ester; cholesterol; LDL-colesterol; apo E