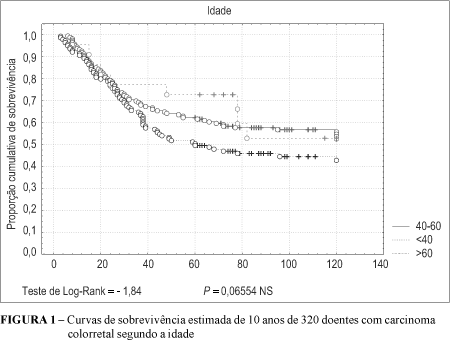
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: The paradoxical evolution of approximately one third of patients with neoplasms cataloged in Dukes stages B and C demonstrates the desirability of utilizing other prognostic criteria that are capable of broadening the information provided by these two important variables. Only a small number of investigators have dedicated themselves to the study of the prognostic value of clinical and macroscopic parameters of colorectal neoplasms, and the results obtained have been shown to be controversial. The principal aim of this work was to evaluate the prognostic importance of these parameters. PATIENTS AND METHODS: A study was made of 320 patients with colorectal cancer who underwent curative extirpation. They had a median age of 58 years, and there were 199 females (62.2%) and 121 males (37.8%). The patients were divided into three age groups: under 40 years old, between 40 and 60 years old and over 60 years old. The tumors were distributed in three intestinal segments: right colon, left colon and rectum. The neoplasms were classified as small (diameter less than or equal to 35 mm) and large (diameter greater than 35 mm). With regard to their form, they were classified as exophytic, when characterized by luminal growth, and endophytic, when there was intramural growth. The involvement of the intestinal circumference at the site of the neoplasm was considered as partial or total. RESULTS: Of the 320 patients, 22 (6.9%) were aged under 40 years, 159 (49.7%) from 40 to 60 years and 139 (43.4%) presented an age of over 60 years. Seventy-three (22.8%) of the neoplasms were located in the right colon, 130 (40.6%) in the left colon and 117 (36.6%) in the rectum. Regarding the size, 280 (87.5%) were large and 40 (12.5%) small; exophytic lesions predominated over endophytic ones - 173 (54.1%) vs 147 (45.9%). A greater number of tumors presented total involvement of the intestinal circumference - 216 (67.5%) - while 104 (32.5%) presented partial involvement. The 5-year survival of the patients was not influenced by their age and sex, or by the location and size of the neoplasms. Exophytic lesions conferred greater survival on their sufferers (65.9%), in comparison with endophytic lesions (49.0%). The survival of patients with lesions partially involving the intestinal circumference was greater than for those with total involvement - 72.1% vs. 51.4%. CONCLUSIONS: Clinical variables had no influence on the patients' prognosis. Among the macroscopic variables, the form of the neoplasia and its involvement in the intestinal circumference did influence the patients' prognosis. These last two variables are important data capable of contributing to the identification of patient subpopulations with greater or lesser prognostic risk.
Colorectal neoplasms; Carcinoma