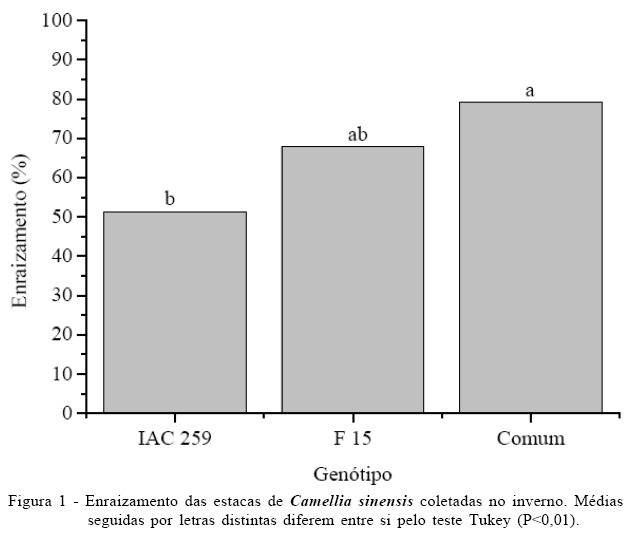
The experiment was 2 carried out to evaluate the effect of cutting collection time, genotype and indolebutyric acid (IBA) on rooting of Camellia sinensis L. cuttings. For such, stems were collected from three genotypes, IAC 259, F 15 and Comum, plants grown in Pariquera-Açu, São Paulo, Brazil, in winter, spring, summer and autumn. Cuttings were prepared and treated with IBA (0, 2.000, 4.000, 6.000 and 8.000 e 10.000mg L-1), planted in vermiculite and kept in greenhouse under 70% shading and periodic irrigation. The experimental design was completely randomized in a factorial scheme 4x3x6 (four times, three genotypes and six concentrations of IBA) with four replicates of eight cuttings. The ideal time to cutting collection was in the winter. Cuttings collected in winter showed average mortality of 41%. In the live cuttings the rooting medium was of 66%, influenced only by the genotype. All had shoots and only 32% had callus. The IBA influenced the number and length of roots in cuttings in winter. In the spring, despite the lower mortality (31%), only 0.34% and 49 % of the live cuttings showed root and shoot respectively, while 97% of the cuttings showed callus. In summer and autumn mortality was extremely high representing 93 and 81% of the cuttings, respectively.
tea; vegetative propagation; IBA