Abstract
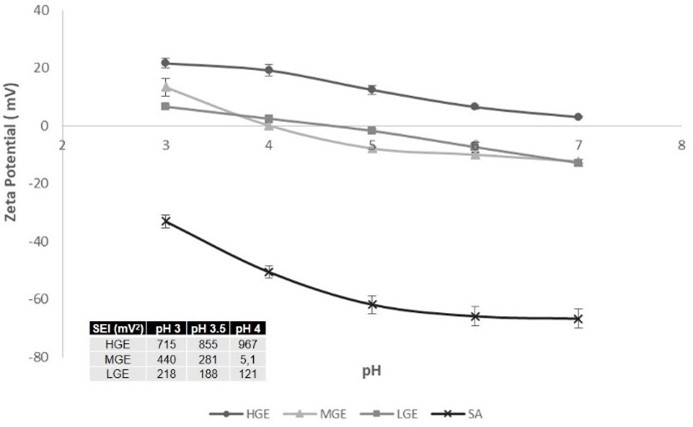
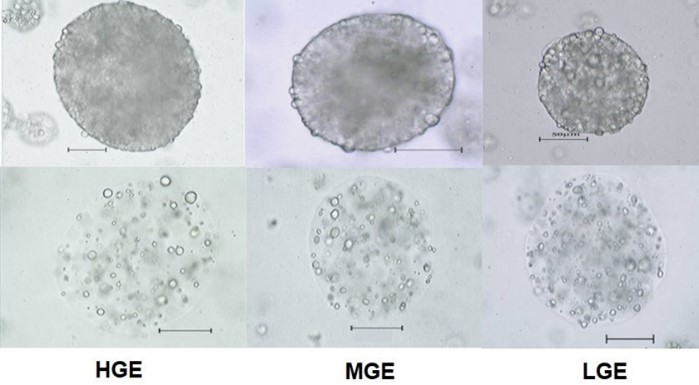
The protein adsorption on the porous alginate microparticles was evaluated in regards to the coating ability and this protective effect during gastrointestinal assay. The coating was performed at suitable pH for optimized electrostatic interaction between protein and alginate. Concentrations of gelatin (HGE) and their hydrolysates (Collagel® (MGE) (> 10 kDa) and Fortigel® (LGE) (3 kDa)) from 1 to 10% (w/w) were tested. Higher protein adsorption was observed in the highest concentration of protein in solution and the amount adsorbed was inversely proportional to the degree of hydrolysis with 47.3, 41.4 and 29.3% of protein adsorbed when HGE, MGE and LGE were used, respectively. The particles that showed higher protein adsorption were submitted to gastrointestinal in vitro assay. In gastric simulation, 39.1, 41.8 and 49.0% of protein from HGE, MGE and LGE were solubilized while 81.3, 61.5 and 95.2% were solubilized after 5 h under enteric conditions.
Keywords:
microencapsulation; ionic gelation; electrostatic interaction; layer-by-layer; protein adsorption

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail