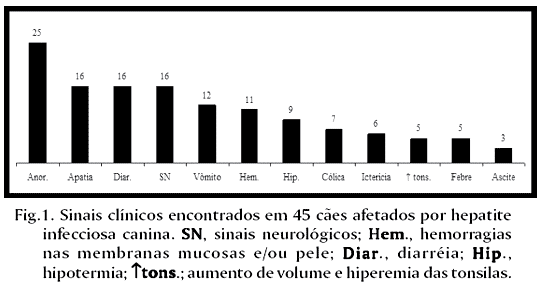
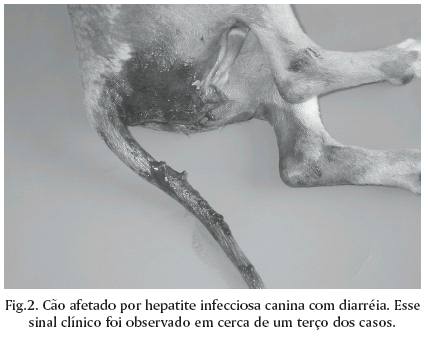
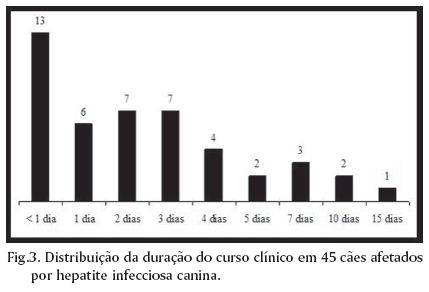
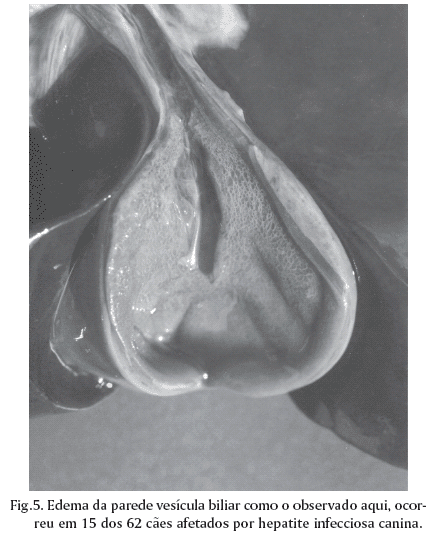
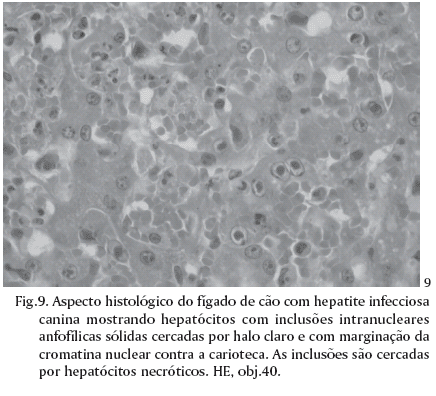
Necropsy reports from 5,361 dogs necropsied over a 43-year period (1964-2006) were reviewed in search for cases of infectious canine hepatitis (ICH). Sixty two (1.2%) cases of the disease were found. Most of the 62 affected dogs (91.9%,) were 2-year-old or less. Clinical signs were recorded in the necropsy files of 45 ICH affected dogs and included anorexia (55.6%), apathy (35.6%), diarrhea (35.6%) (often with blood [43,8%]), neurological signs (33.3%), vomiting (26.7%), petechiae and echymosis in the mucous membranes and/or skin (24.4%), hypothermia (20.0%), abdominal pain (15.6%), icterus (13.3%), enlargement and congestion of the tonsils (11.1%), fever (11.1%) and ascites (6.7%). The clinical courses lasted from few hours to 15 days. The most frequent necropsy findings included hepatic changes (87.1%), edematous, congested and hemorrhagic lymph nodes (51.6%), bloodstained fluid, clear fluid or whole blood in the abdominal cavity (35.5%), and petechial or paint-brush hemorrhages over the pleural (27.4%) and gastrointestinal (24.2%) serosal surfaces. In 12.9% of the cases there was a granularity to the intestinal serosa. Hemorrhages in the leptomeninges and in the substance of the brain were observed in 9.7% of the cases. Hepatic gross changes included moderately enlarged and more friable livers with marked lobular pattern, congestion and multifocal pale or hemorrhagic foci of necrosis. Films and strands of fibrin covered the hepatic surface in 20.4% of the cases and in 27.8% of the cases the gall bladder was thickened by edema. Zonal or randomly distributed multifocal hepatic necrosis (93.5%) associated with intranuclear inclusion bodies were the most consistent microscopic findings. Intranuclear inclusion bodies were found in the liver in every case and their detection was the criterium for confirmation of the diagnosis. The most significant microscopic extra-hepatic lesions included hemorrhages and intranuclear inclusion bodies in endothelial and reticuloendothelial cells of the renal glomeruli (50.0%) lymph nodes (47.8%), brain (27.8%), tonsils (25.0%) and spleen (10.0%).
Liver diseases; viral diseases; infectious diseases; pathology; diseases of dogs; infectious canine hepatitis