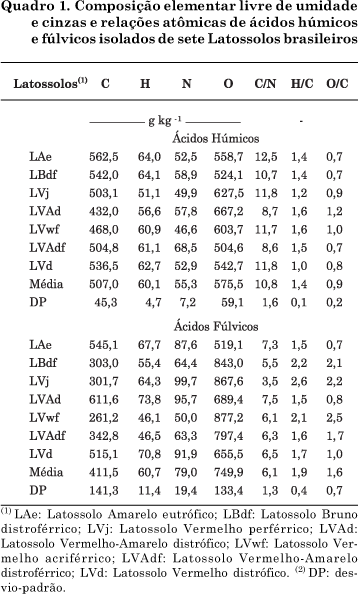
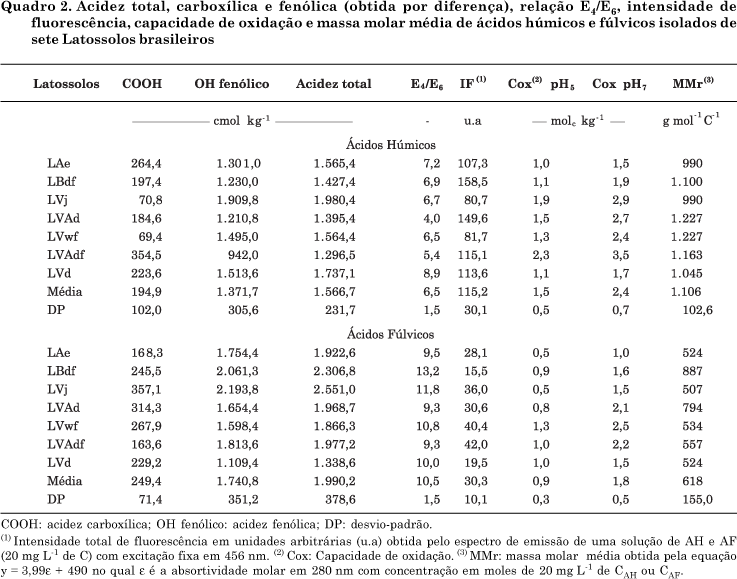
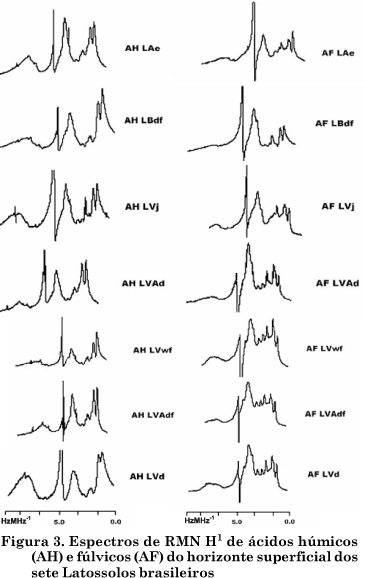
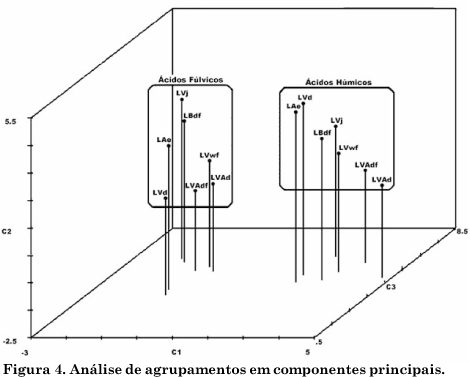
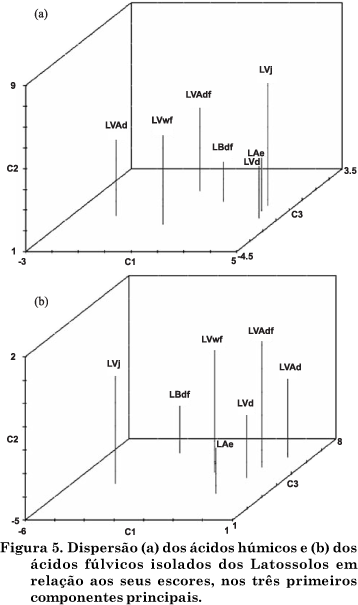
The determination of structural characteristics of humic substances (HS) is essential to understand the behavior of surface chemistry of highly weathered soils. Humic acids (HA) and fulvic acids (FA) isolated from the surface horizon of seven Oxisols of different locations of Brazil were characterized by analyses of elemental composition, total and carboxylic acidity, oxidation capacity and spectroscopic techniques. The oxidation degree of the humic substances was high, while acidity and molecular weight were relatively low, indicating a very reactive alkaline soluble organic matter. Compared with HA, the C content of FA was lower and oxygen content higher. The E4/E6 ratio values were high and the molar mass was estimated at 1.106 and 618 g mol-1 for HA and FA, respectively. The lower molar mass observed for FA was consistent with the lower chemical complexity detected by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), showing fewer well-defined spectral bands. The results of ¹H-nuclear magnetic resonance (H-NMR) spectroscopy indicated more hydrophobic H in HA and a high amount of H bonded with O in FA, consistent with the higher acidity and solubility at any pH value. Despite the similar chemical functionality found, both HA and FA, most humic substances could be distinguished by the principal component analysis, indicating distinct chemical attributes of the humic fractions.
organic matter; spectroscopy; humic substances; tropical soils