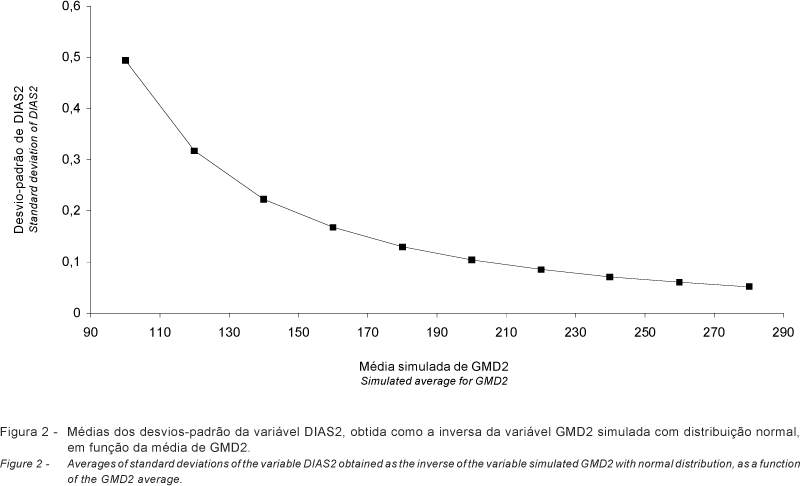
Four simulation studies were conducted to verify the distribution of the inverse of variables with normal distribution, relatively to variances, averages, truncation points and sample sizes. The variables simulated were GMD, with normal distribution and representing average daily gain, and DIAS defined as a multiple of the inverse of GMD and representing days to reach a fixed body weight. The SAS® (1990) system was used, for simulation of the data, and for subsequent analysis of the results in all studies. The standard deviations simulated for GMD significantly affected DIAS sampling averages. The regression analyses showed a reduction on the mean and in the standard deviation of DIAS as a function of the increase in the average of GMD. Including a truncation point at about 10 to 25% of the mean value reduced the mean of GMD and increased the mean of DIAS when the coefficient of variation of GMD was above 25%. Size of the groups did not significantly affect averages of GMD or DIAS. Standard deviation and CV of GMD increased with the increase on group size. Due to the dependence between the average and the standard deviation and the variation observed in the standard deviations of DIAS as a function of group size, the use of DIAS as selection criteria may reduce the accuracy of the genetic evaluation. Therefore, in order to substitute GMD by DIAS, it is necessary the use of a method of analysis robust enough to eliminate the heterogeneity of variance.
beef cattle; selection criteria; bayesian inference; average daily gain