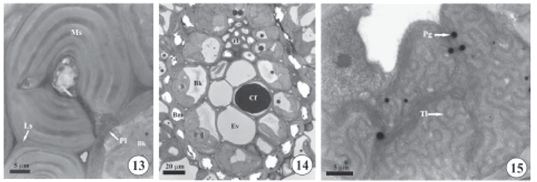
Anatomical and ultrastructural aspects of Cyperus maritimus Poir. were analyzed with the aim of identifying adaptive features for the dune environment. Collections were made at Pipa beach, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Leaves were submitted to different analyses: light microscopy, scanning and transmission electron microscopy. In frontal view, the epidermis has unicellular trichomes, silica bodies, a striate cuticle and wax deposits. In transverse section, the epidermis is uniseriate with thickened outer periclinal walls. The stomata are paracitic and the pore sometimes obstructed by wax. Under the adaxial epidermis, there are several layers of aqueous parenchyma. The vascular bundles occur in multiple rows, the peripheral row having bundles with narrower diameters than the central row. Characters related to Kranz syndrome of the chlorocyperoid type were observed. Ultrastructural features support a possible C4 pathway in this species. This work is the first citation of chloroplasts in the cells of the vascular system for the genus. In this study, it was possible to observe several important features of plants submitted to water and salt stress, such as: wax, thickened outer periclinal walls of the epidermal cells, aqueous parenchyma and Kranz syndrome.
Cyperus; Kranz; anatomy; ultrastructure; salinity