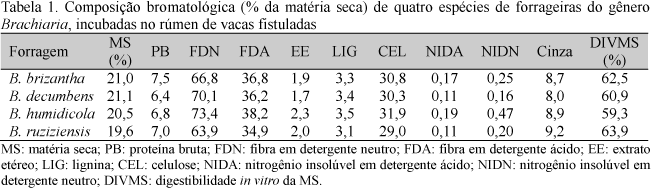
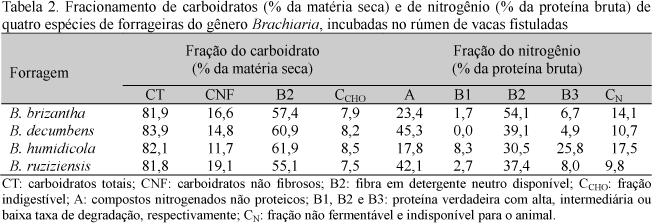
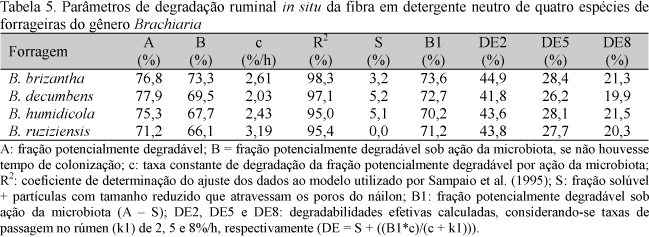
The chemical composition and the ruminal in situ degradability of dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), and neutral detergent fiber (NDF) of four species of Brachiaria were evaluated. The forages were harvested at 56 days of growth. Three rumen-fistulated crossbred Holstein × Zebu cows were used. The chemical composition of B. brizantha, B. decumbens, B. ruziziensis, and B. humidicola forages were, respectively: 21.0, 21.1, 20.5, and 19.6% for DM; 7.5, 6.4, 6.8, and 7.0% for CP; and 66.8, 70.1, 73.4, and 63.9% for NDF. B. ruziziensis presented the best nutritional value among the Brachiaria species, as indicated by the highest effective degradability (ED) and ruminal degradation rates of both DM and CP. B. ruziziensis also showed the highest NDF ruminal degradation rate and the lowest NDF concentration. In contrast, B. humidicola showed the worst nutritional composition, as indicated by the lowest DM and CP ED values and the highest content of indigestible and fibrous fractions.
cattle; Brachiaria decumbens; Brachiaria brizantha; Brachiaria humidicola; Brachiaria ruziziensis