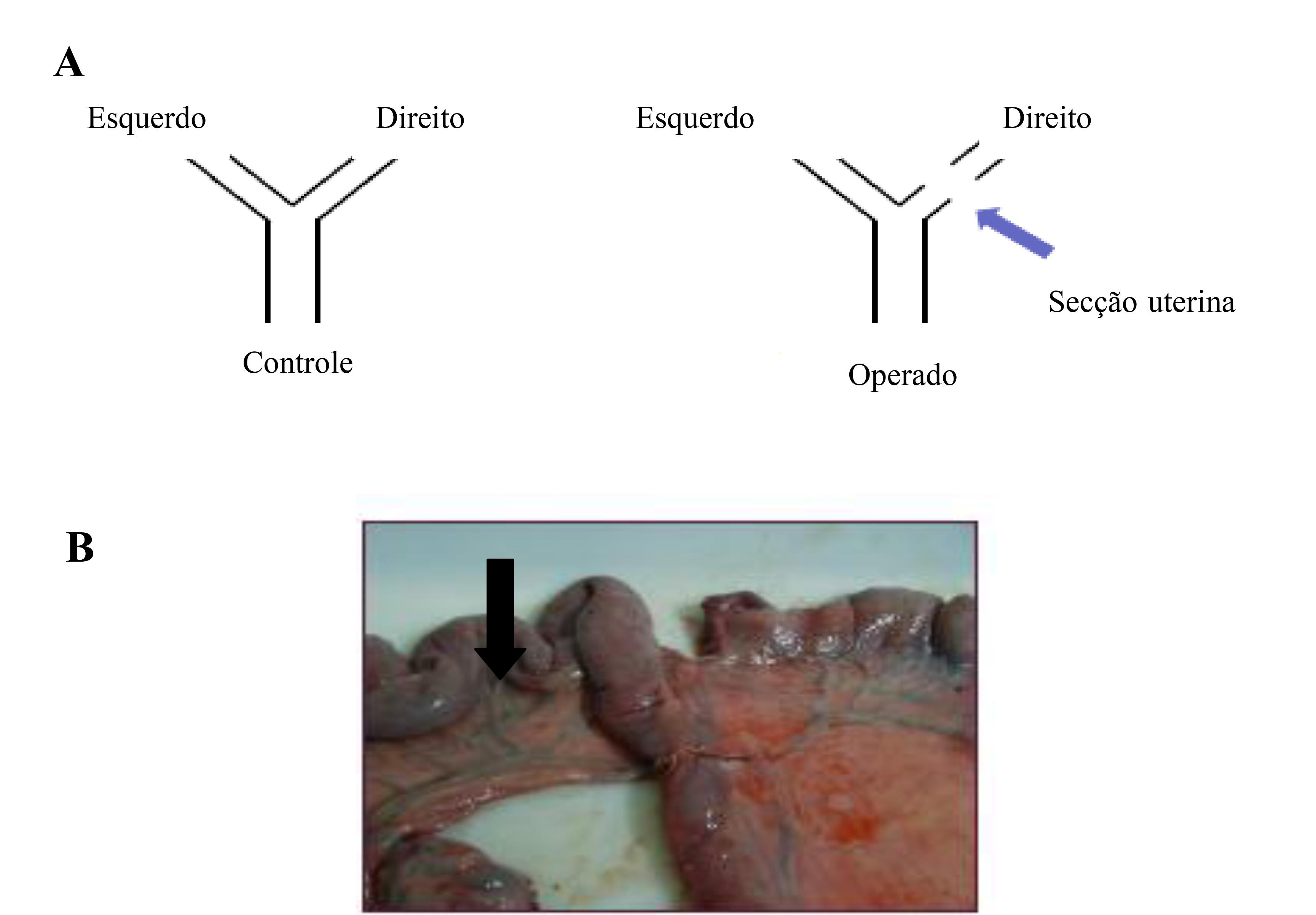
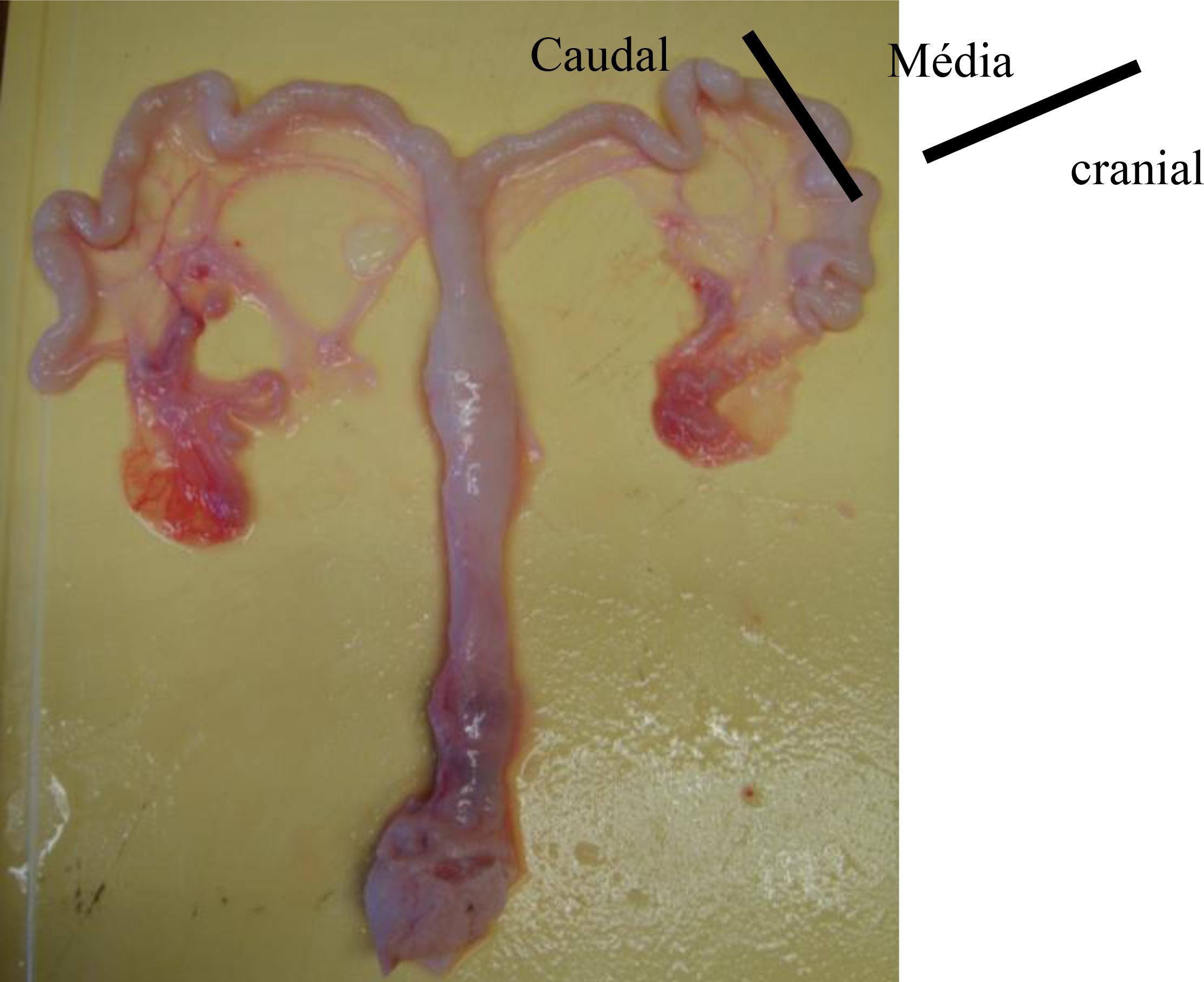
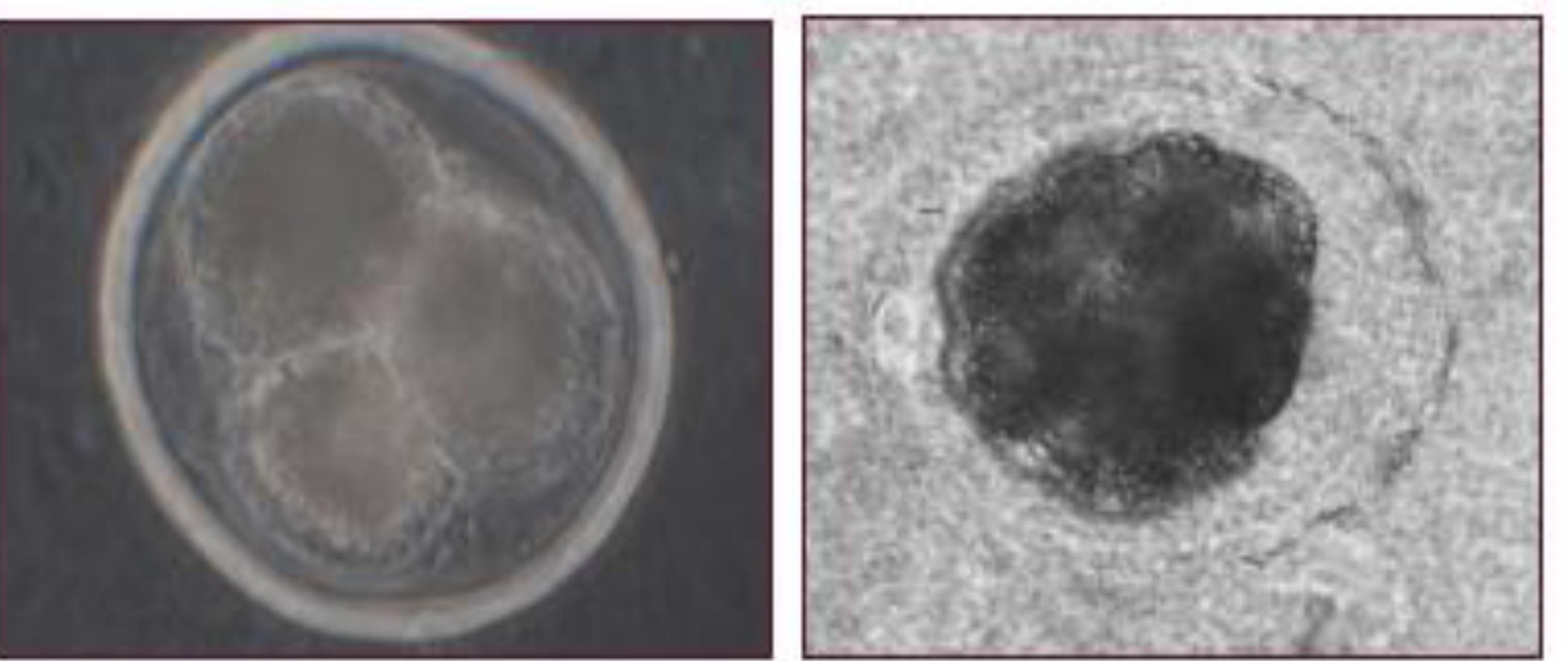
Deep intrauterine insemination (DUI) is of great importance for the swine industry as it can increase the efficiency in the use of boars of high genetic merit, and facilitate the use of biotechnologies such as frozen and sexed semen. However, a better understanding of the mechanisms by which the sperm colonize the uterine tubes is essential. The aim of the present study was to investigate the existence of intrauterine sperm migration after DUI in one uterine horn, through the fertilization of oocytes in the contra lateral uterine horn. Fourteen multiparous sows were divided into two experimental groups: Operated (n = 7), where females had a segment close to the base of the uterine horn surgically removed, and Control (n = 7), females with intact uterus. Both groups were inseminated through DUI and slaughtered 5±1.2 days after the last insemination. The reproductive tracts collected were dissected and the number of corpora lutea counted in both ovaries. Embryo recovery was performed though flushings of uterine tubes and horns with Phosphate Buffered Saline solution and further examination under a dissecting microscope. Embryos were found in the uterine horns of both sides of the reproductive tract in both experimental groups. In the operated group, just one female had embryos in only one side of the reproductive tract. The results presented herein suggest that sperm migration in pigs may occur both in a retrograde way through the uterus and by intraperitoneal migration. These findings will certainly contribute to increase the efficiency of the DUP technique, which is of great importance for the improvement of the swine industry.
pigs; deep intrauterine insemination; sperm migration