Abstract
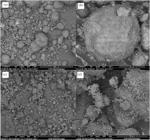
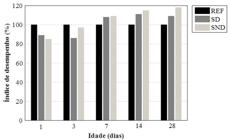
The silica fume is commercially available in densified form (DS) when subjected to particle agglomeration processing to reduce its volume during transport, or undensified (US) when that process does not occur. The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether the densification of silica fume can influence the properties of cementitious materials. With that purpose, the effect of replacing 10% of Portland cement CP V-ARI by US and DS was investigated. Compressive strength tests were performed on the microconcrete at 1, 3, 7, 14 and 28 days. To explain the mechanical behaviour of the microconcrete, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS) tests were performed on the cement pastes. Due the smaller particle size and the higher specific surface of the US compared to the DS, there was a change in the microstructure of the cement pastes. The US provided a higher consumption of calcium hydroxide (CH) and a lower calcium/silica (Ca/Si) ratio in the cementitious matrix, resulting in a higher compressive strength in the microconcrete with US compared to that with DS. The study concludes that US is more effective when used in the production of cementitious materials.
Keywords:
Portland cement; Pozzolanic materials; Microstructure; Densified silica fume and undensified silica fume

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail





