Abstract
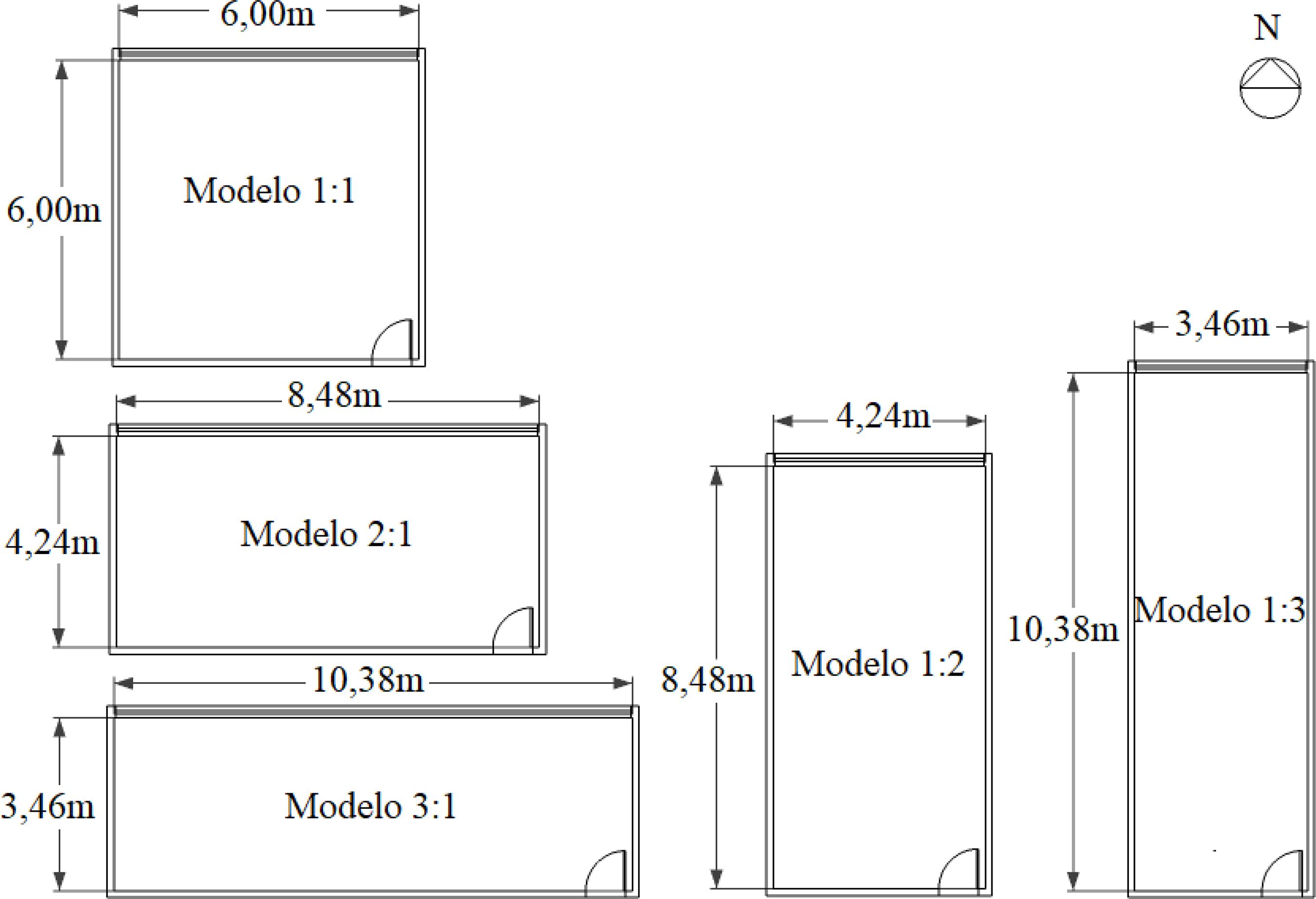
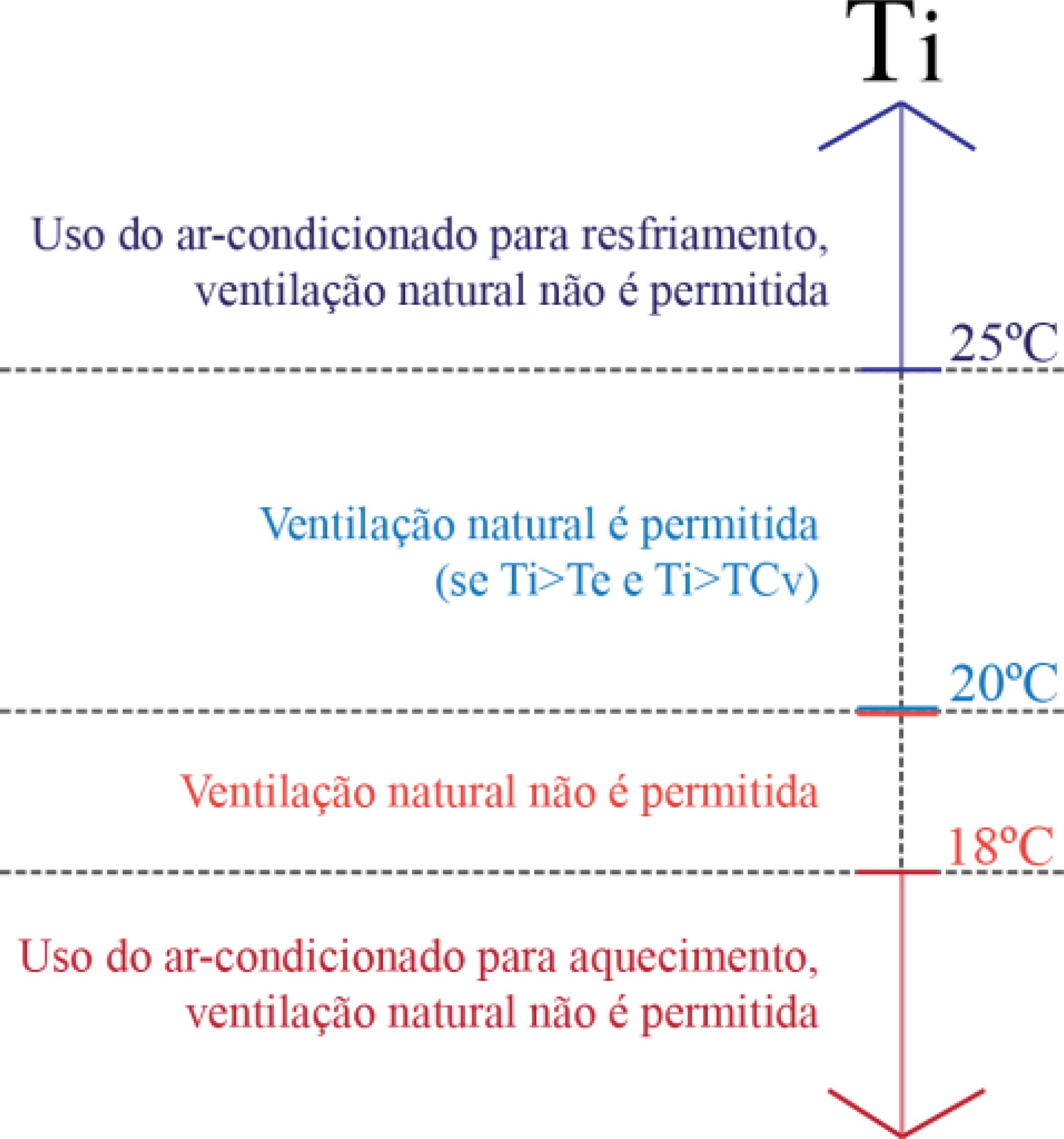
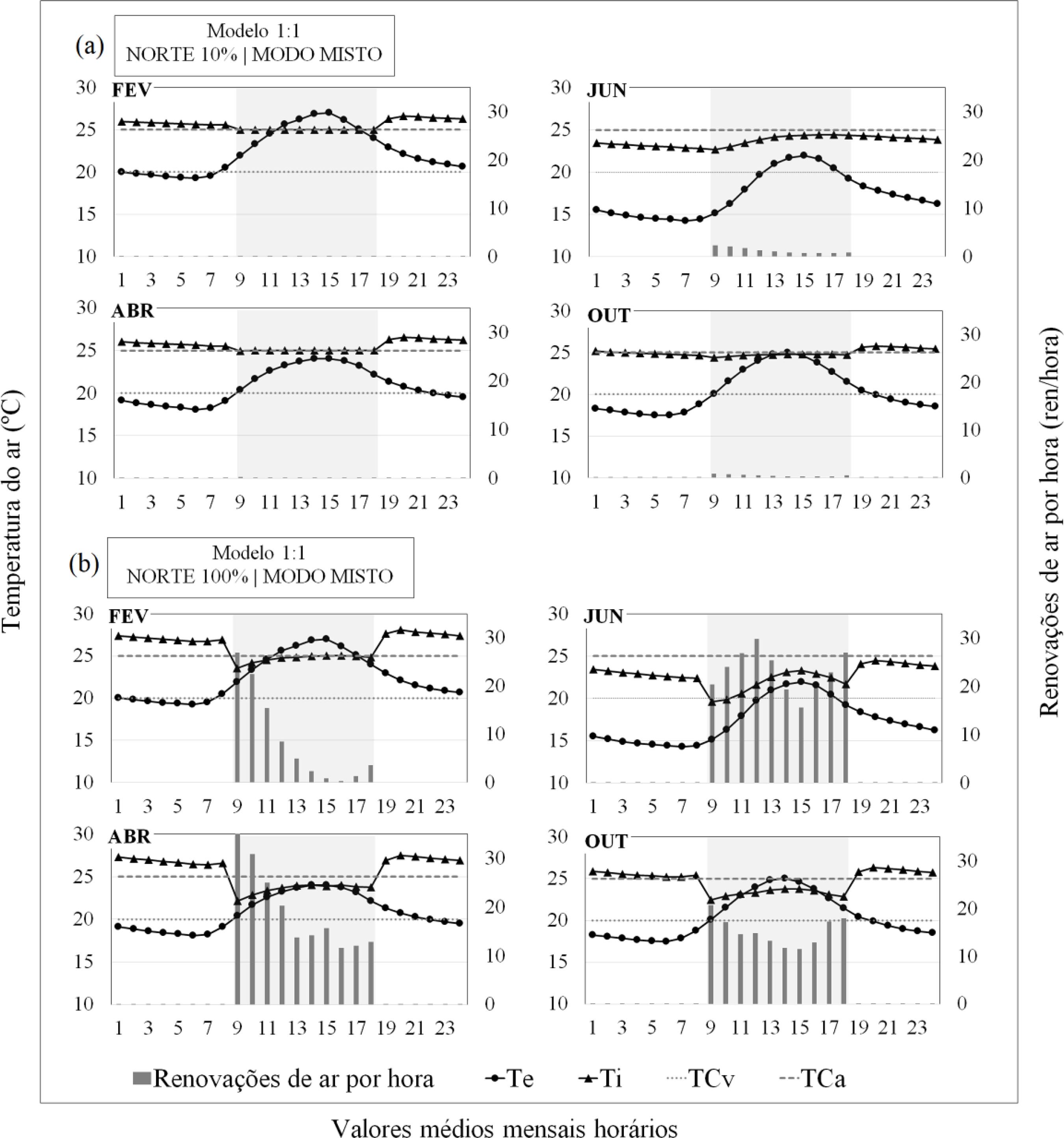
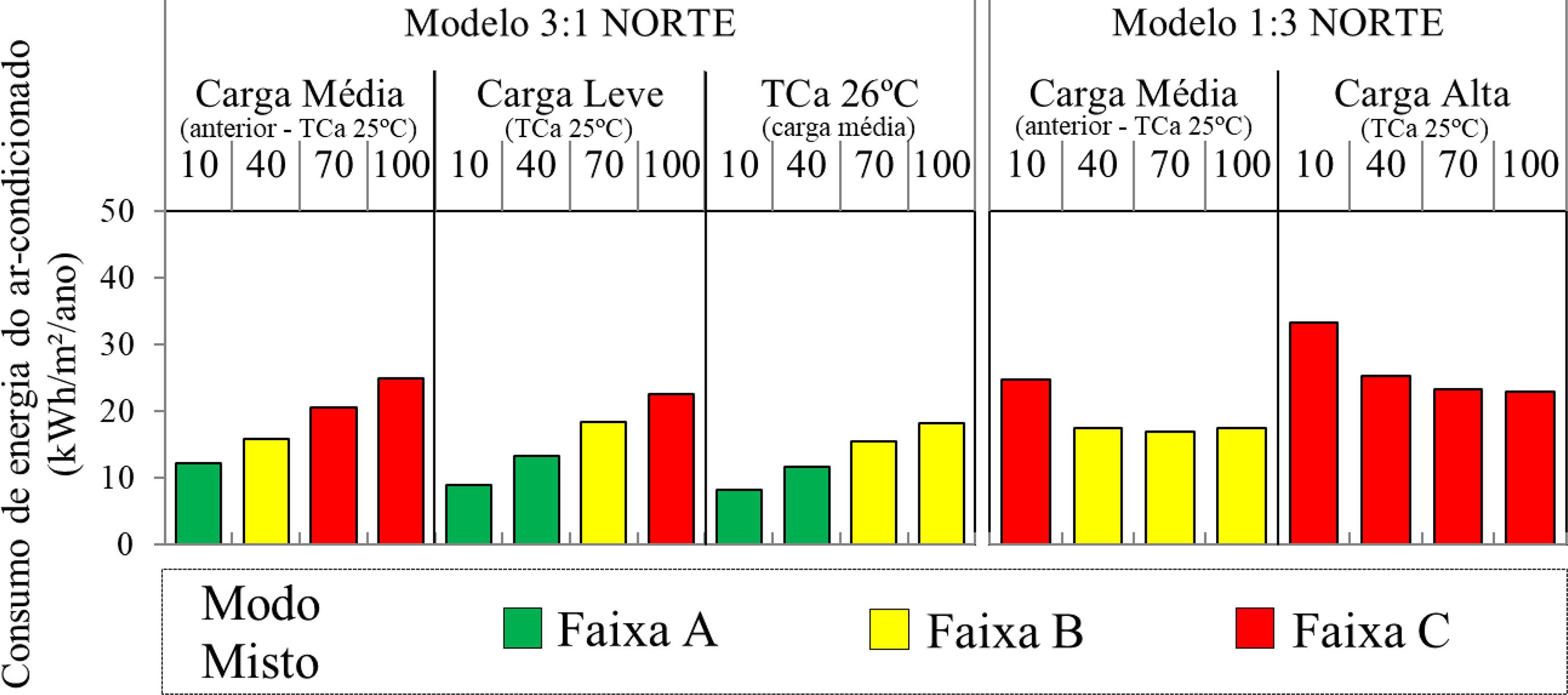
The literature presents only a limited number of studies on mixed-mode air-conditioned buildings (or with hybrid ventilation) with simple design strategies. Thus, this project evaluates the impact of architectural (room shape, window size and orientation) and usage parameters (equipment load density and air conditioning activation temperature) on the thermal performance of mixed-mode cellular offices in the city of São Paulo. The method consisted in characterising the studied models using a data survey of this building type and parametric computer simulations using the EnergyPlus software. The method demonstrated that hybrid ventilation led to a decrease of up to 52% in the energy consumption of the air conditioning used for cooling. When adopting such strategy, it is important to associate the room's shape to the window area. Lower energy consumption levels were observed for the combinations of deep and narrow rooms with larger windows or less deep and wider rooms with smaller windows. However, the decrease in the effective area for ventilation changed these conclusions, always yielding lower energy consumption with smaller windows. Hence, this study indicates that an adequate combination of parameters can result in designs that consume less energy, assisting in the design of this type of building.
Keywords:
Energy consumption; Hybrid ventilation; Mixed-mode; Office buildings; Computer simulation

 Fonte: adaptada de EPvieW (
Fonte: adaptada de EPvieW ( Fonte: adaptada de EPvieW (
Fonte: adaptada de EPvieW (