Abstract
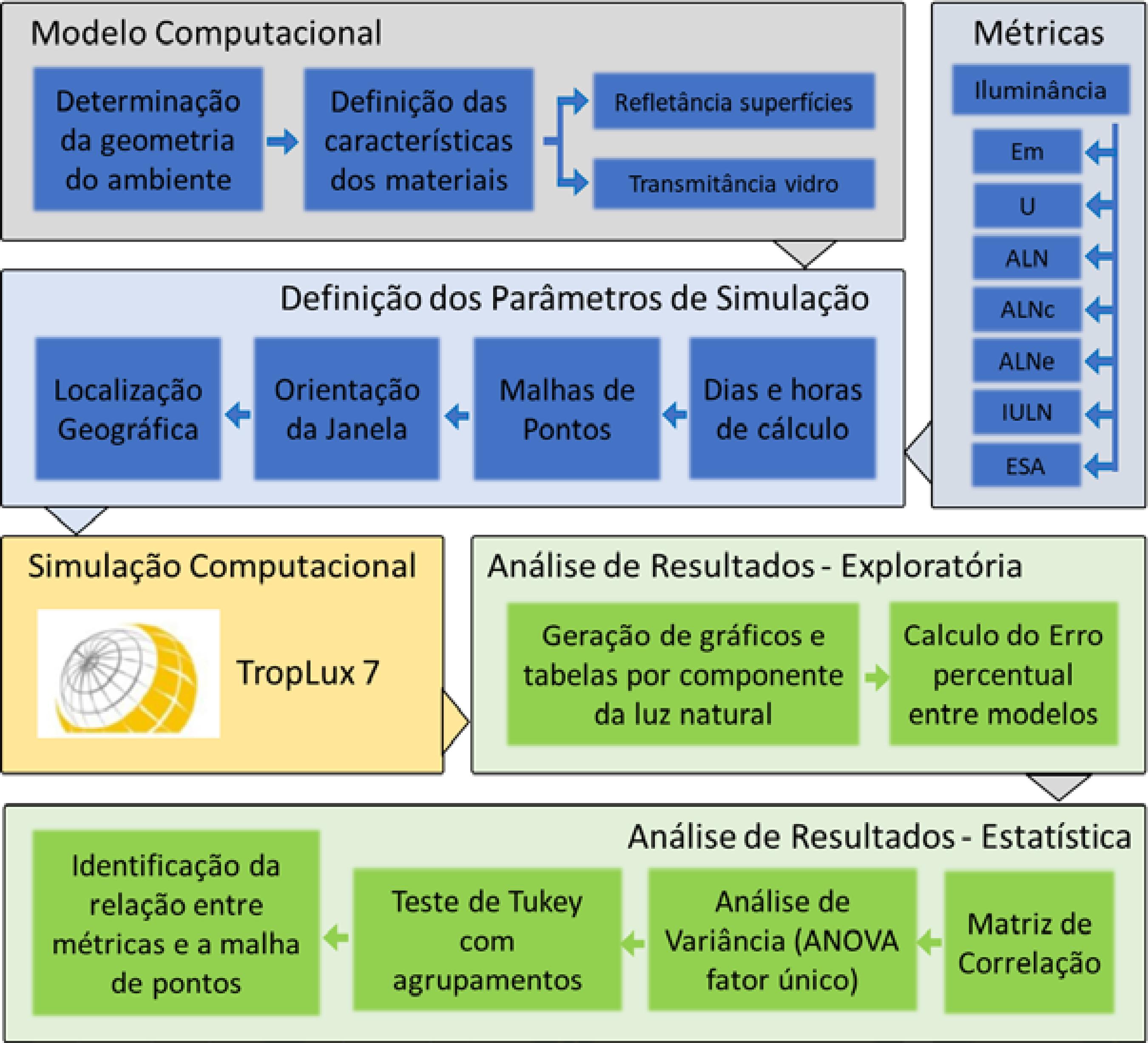
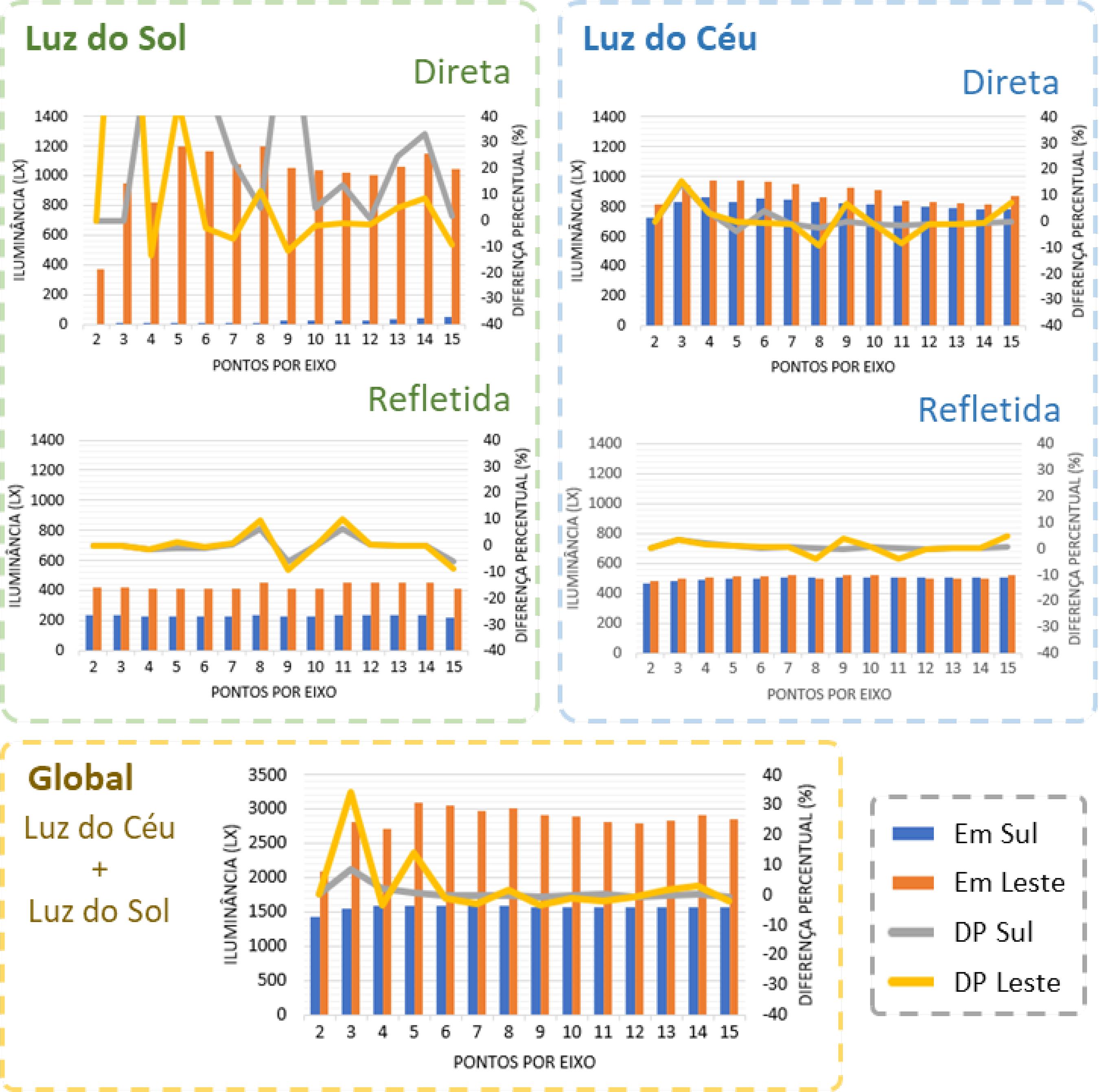
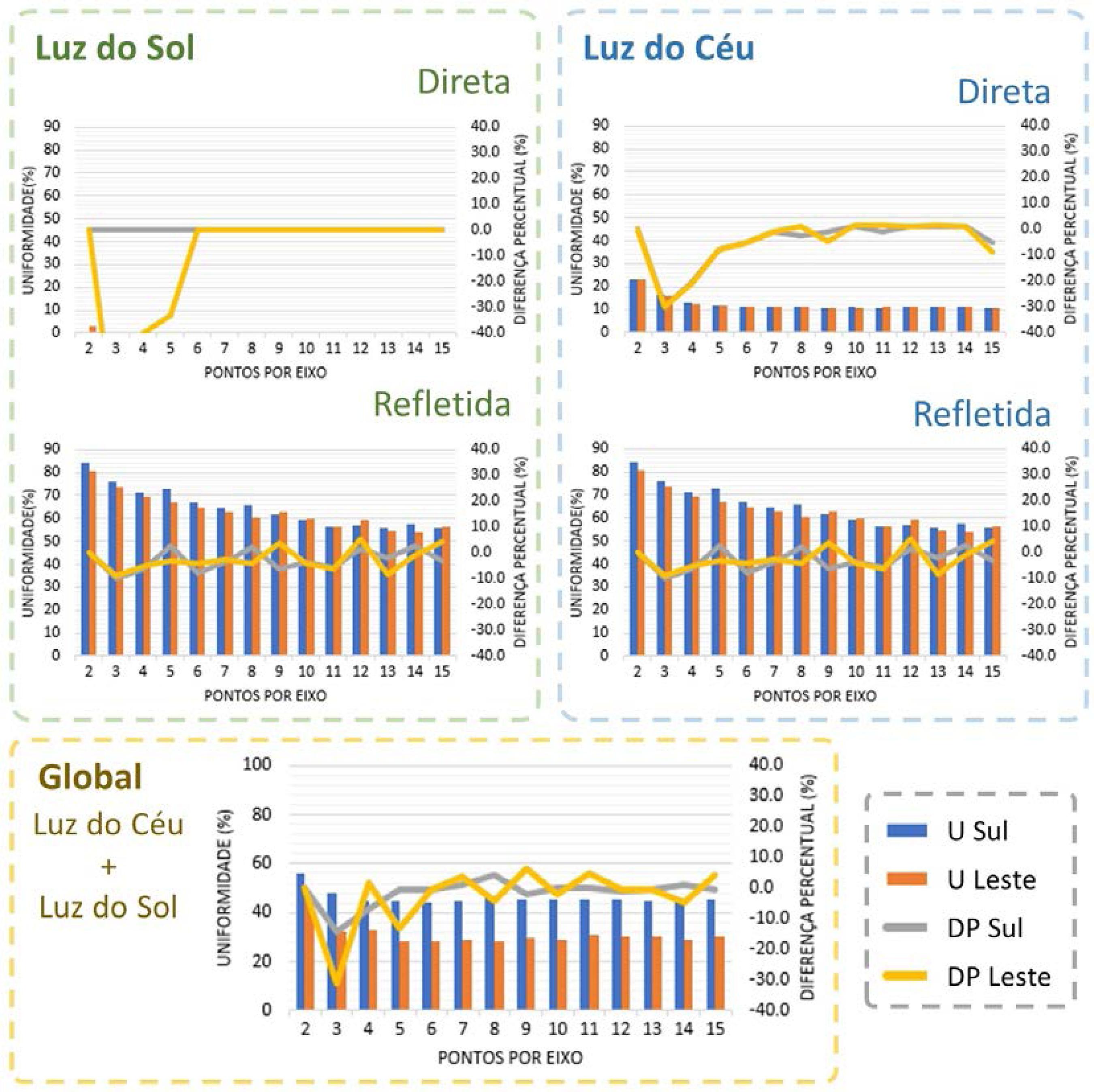
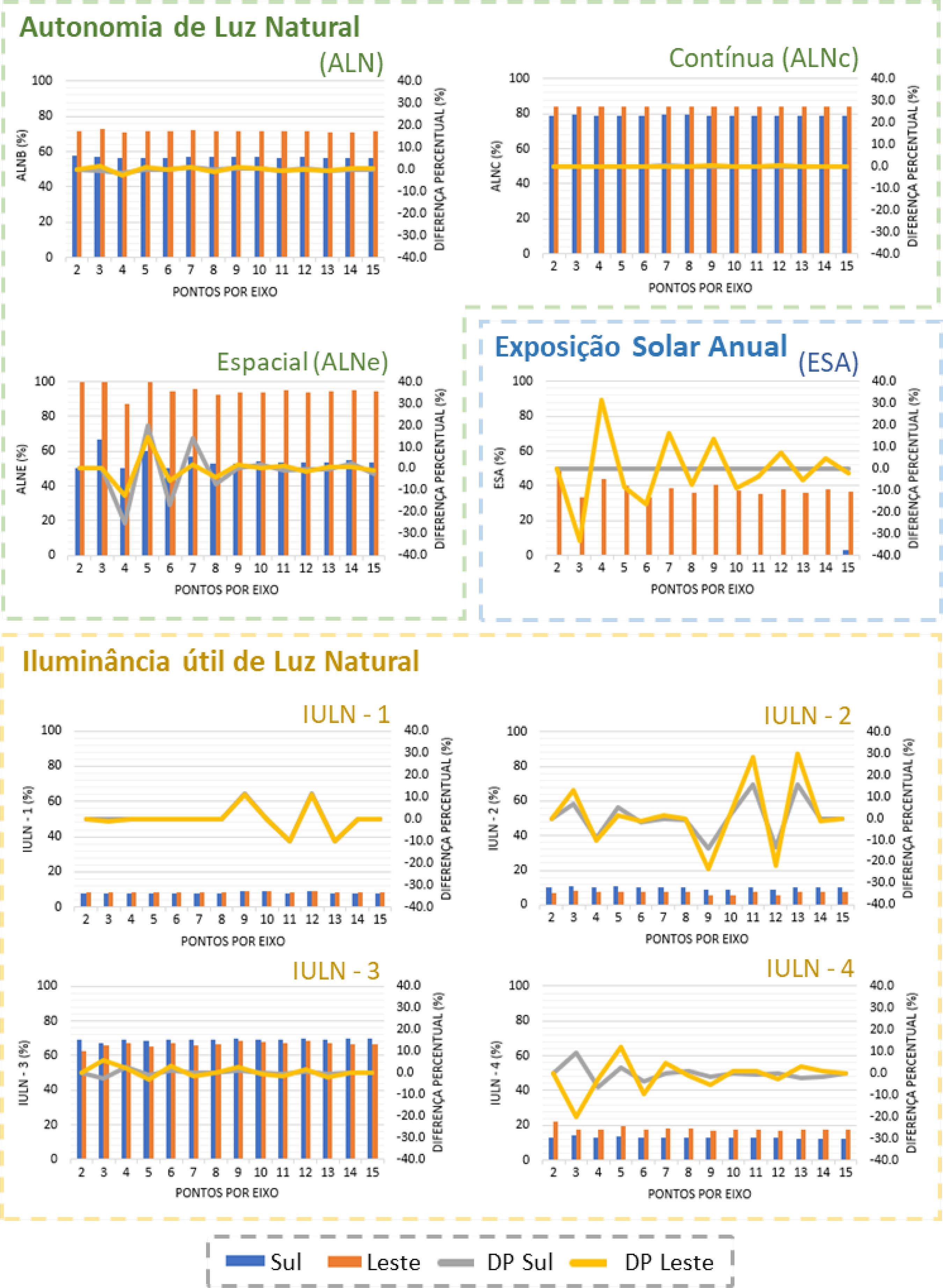
The luminous performance of buildings can be evaluated using several tools, most of them based on illuminance. Although progress has been made in daylight metrics in recent decades, mainly due to developments in computer systems technology, they do not usually address how grids are defined. This paper analyses the influence of the grid influence on the performance of the following metrics: average illuminance (Em), uniformity (U), daylight autonomy (DA), continuous daylight autonomy (cDA), spatial daylight autonomy (sDA), useful daylight illuminance (UDI) and annual solar exposure (ASE). Daylight simulations were done using TropLux, in a 6x6 m2 room without shading device. Exploratory and statistical analyses were performed using the ANOVA method, Tukey tests and a correlation matrix. The results indicate that the grid of points influences on the precision of the studied metrics. For Em, U, DA, cDA, sDA and UDI, the results stabilised starting from a 6x6 grid with a 1,00m distance between points. For ASE, a grid with 11x11 points, or a 0.54 m distance between points was required. This study suggests that a different analysis of skylight and direct sunlight, taking into account grid size, may optimise computer performance maintaining accuracy.
Keywords:
Daylighting; Grid of points; Daylight metrics; Computer simulation