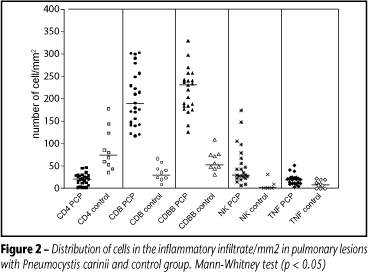
OBJECTIVES: It has been experimentally demonstrated that host defense against Pneumocystis carinii depends on complex interactions within host immune response, mainly CD4 lymphocytes and alveolar macrophages. Since this is an important agent related to immunodeficiency, our purpose was to characterize the inflammatory immune response in lung from necropsy of AIDS patients. PROCEDURES: Twenty-five necropsies with diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia were selected for immunohistochemical investigation of CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes, macrophages (CD68+), NK cells (CD57+) and cells expressing TNF-alpha. The immunostained cells were quantified and statistically analyzed. RESULTS: All specimens presented a great number of cysts of Pneumocystis carinii in alveoli, as well as septal enlargement with inflammatory infiltrate constituted predominantly by lymphocytes and macrophages. CD4+ T cells were decreased in number, and CD8+ T cells, NK cells and macrophages predominated. Cells expressing TNF-alpha were frequently observed in septal inflammatory infiltrate. CONCLUSIONS: The immunosupression related to AIDS induces a reduction in the number of CD4+ T cells and influences high-level parasitism. The cell components that characterize the inflammatory infiltrate contribute to the severe lung injury of those patients.
Pneumocystis carinii; Immunohistochemistry; Cellular immune response