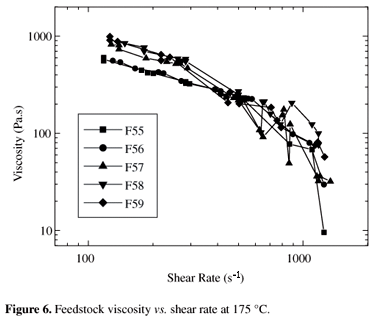
The rheological behavior of alumina molding feedstocks containing polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinylbutyral (PVB) and stearic acid (SA) and having different powder loads were analyzed using a capillary rheometer. Some of the feedstocks showed a pseudoplastic behavior of n < 0, which can lead to the appearance of weld lines on molded parts. Their viscosity also displayed a strong dependence on the shear rate. The slip phenomenon, which can cause an unsteady front flow, was also observed. The results indicate that the feedstock containing a lower powder load displayed the best rheological behavior. The 55 vol. % powder loaded feedstock presented the best rheological behavior, thus appearing to be more suitable than the formulation containing a vol. 59% powder load, which attained viscosities exceeding 10³ Pa.s at low shear rates, indicating its unsuitability for injection molding.
alumina; rheological behavior; ceramic injection molding