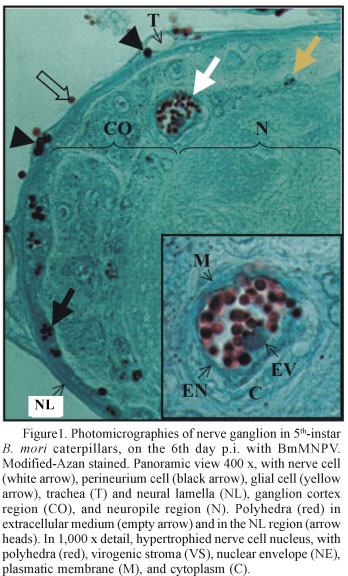
BmMNPV, a Nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from infected Bombyx mori (L.) larvae in Paraná State - Brazil, was used to inoculate healthy 5th-instar B. mori larvae and examine the infection on central nervous system (CNS) cells. Samples of nervous tissue were removed from the infected insects, at different sampling times, and processed for cytopathology studies by light and transmission electron microscopy using routine techniques. The experiment included both inoculated and non-inoculated larvae (control). BmMNPV infection was detected on the 5th day after inoculation in CNS cells. Initially, infection was characterized by nuclear hypertrophy and the presence of virogenic stroma, in which the progeny virions were produced. Virions are enveloped and occluded into protein crystal, the polyhedra. Lyses of infected CNS cells were undetected; however, free mature polyhedra were seen in spaces inside the CNS. These polyhedra possibly came from trachea that penetrate the CNS and its cells, which are susceptible to BmMNPV and lyses after infection. We conclude that the tracheal system is responsible for disseminating BmMNPV infection in B. mori CNS and that the tracheal branches allow non-occluded virions to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
Insect; silkworm; Baculoviridae; neural lamella; perineurium