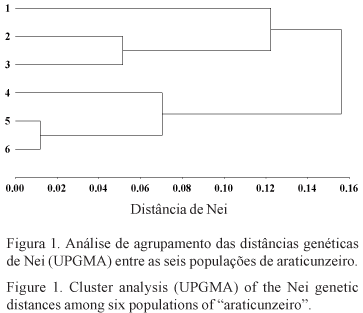
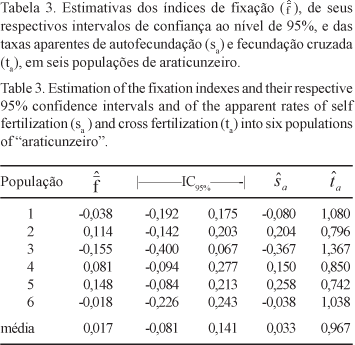
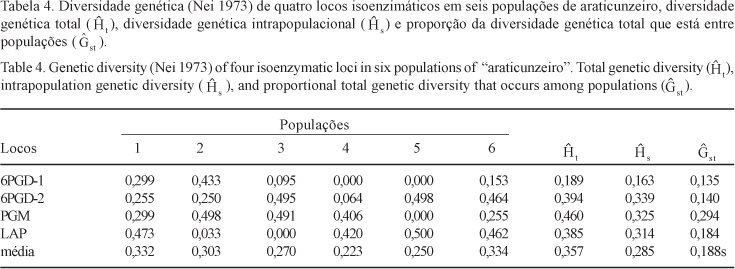
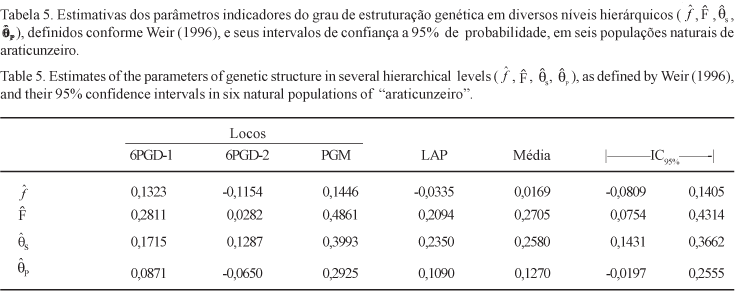
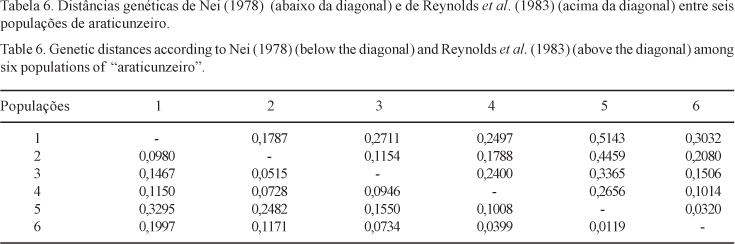
The level and distribution of the genetic variability in natural populations of "araticunzeiro" were estimated using a sample of six natural populations, collected in two different regions of the State of Goiás, Brazil. Samples comprising 30 individuals from each population were genetically evaluated for four allozyme loci: 6-Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase (6PGD), Phosphoglucomutase (PGM), Malate Dehydrogenase (MDH) and Leucine Aminopeptidase (LAP). Two dimeric loci were detected for the 6PGD isozyme system while all the other systems evaluated showed typical monomeric loci pattern. No polymorphism was detected for the MDH enzymatic system. The estimated average number of alleles per polymorphic loci was two. The estimated total heterozygosity (averaged across loci) was 0.357, suggesting that a high level of genetic variability is present in the species along the sampled geographic region. About 19% of the total genetic variation was found to be due to differences at the population level, suggesting the existence of a high genetic divergence among populations. Accordingly, the analysis of variance of allelic frequencies for each polymorphic loci showed a strong genetic structure at the population level. Significant values for the average coefficients of coancestry among individuals within populations and for total inbreeding were found. The genetic divergences between pairs of populations showed to be partially correlated to the geographic distances between pair members. Results obtained here suggested that A. crassiflora is preferentially alogamous, in conformity with other authors findings.
Annona; cerrado; genetic characterization; isozyme