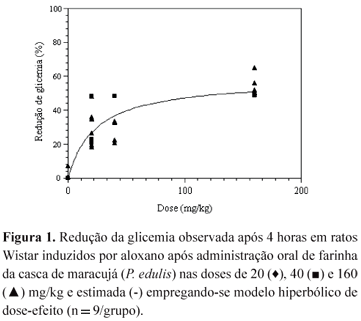
This study goals the pharmacodynamic modeling of anti hyperglycemic action of flour of Passion fruit bark (Passiflora edulisSims, Passifloraceae) in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. The animals were divided into three groups (n = 9) that received different doses: 20, 40 or 160 mg/kg of flour. The blood samples were collected from the tail vein and the blood glucose was determined using a glucometer Prestige IQ in 0, 1, 2, 4 and 6 h after the oral treatment. It was observed that the effect of the flour of Passion fruit bark was dose dependent, getting an expressive effect observed in four hours from all doses tested, being more pronounced at the 160 mg/kg dose. This effect was expressed as reduction of basal blood glucose in respect to zero time and can be modeled through a classic dose effect model. It allowed the determination of maximum effect (Emax) and the necessary dose to reach 50% of this effect (ED50). After the data modeling, it was gotten a value of Emax = 58,41% and ED50 = 23,61 mg/kg. This approach allows the comparison of antyhyperglicemic effect of Passiflora eduliswith other species that present activity lowering the glycemia, through the presence of soluble fibers.
Passiflora edulis; hidrossoluble fibers; antihyperglycemic; pharmacodynamic model; alloxan