Abstract
Objective:
The aim of the present study was to estimate the prevalence of disability and associated factors in elderly stroke survivors.
Methods:
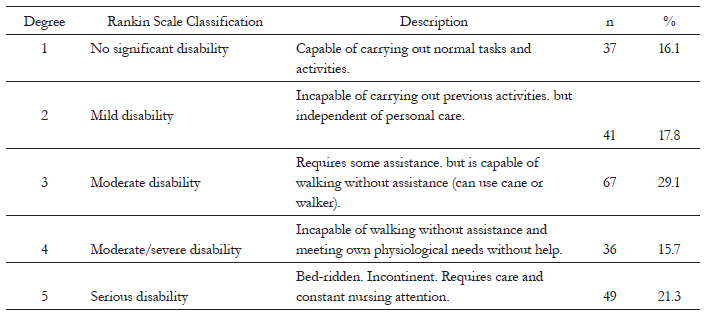
A cross-sectional study of 230 elderly persons was conducted in the 22 territories of the Estratégia de Saúde da Família (the Family Health Strategy) of Vitória, in the state of Espirito Santo. Patients were assessed using the modified Rankin Scale. Poisson regression with robust variance in crude and adjusted analyses was employed.
Results:
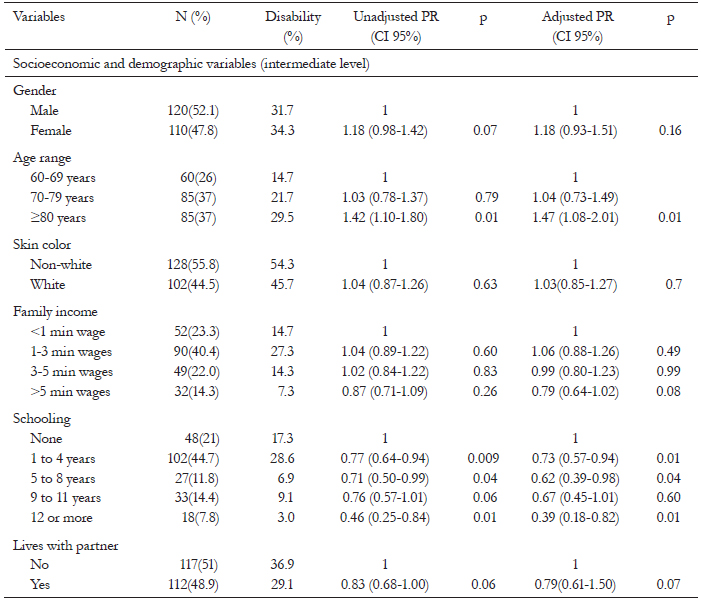
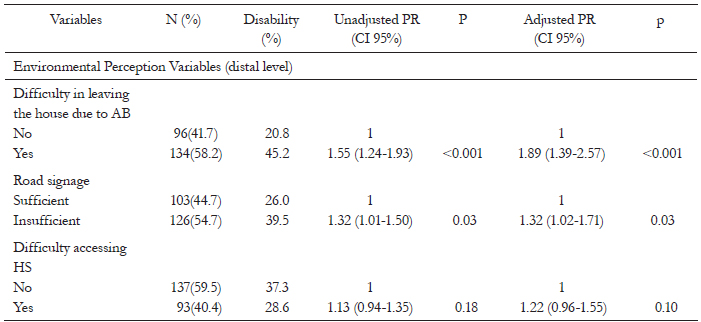
The majority of subjects were men (52.1%) aged between 60 to 98 years, with a mean age of 75.8 (sd±9.2). The prevalence of disability was 66%. Age ≥80 years, self-perceived limitations in bodily function, considering the physical structure of the street to be a barrier to leaving home and believing street lighting to be insufficient were positively associated with functional disability. Possessing 12 or more years of schooling was inversely associated with the outcome.
Conclusions:
The high prevalence of disability and associated factors in elderly stroke survivors reinforce the need for a health system that operates continuously and proactively, promoting active aging.
Keywords:
Elderly; Stroke; Family Health Strategy; Aging; Primary Health Care; Public Health.