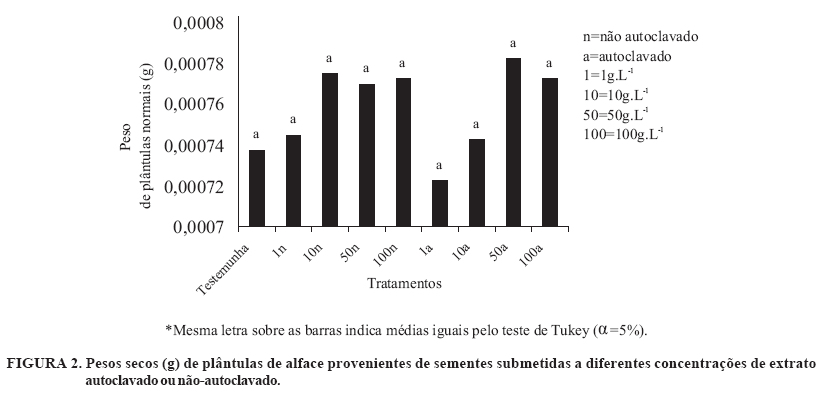
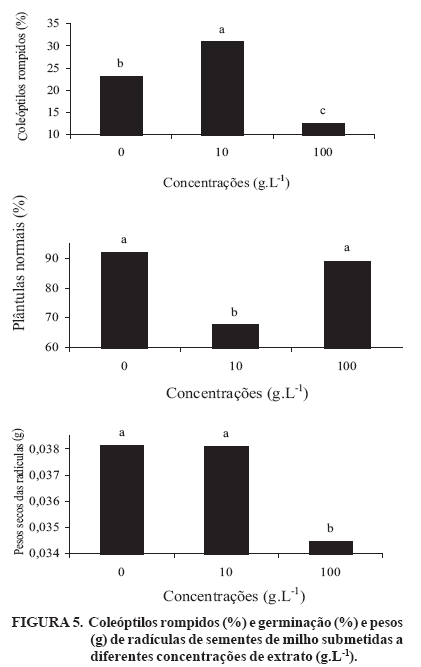
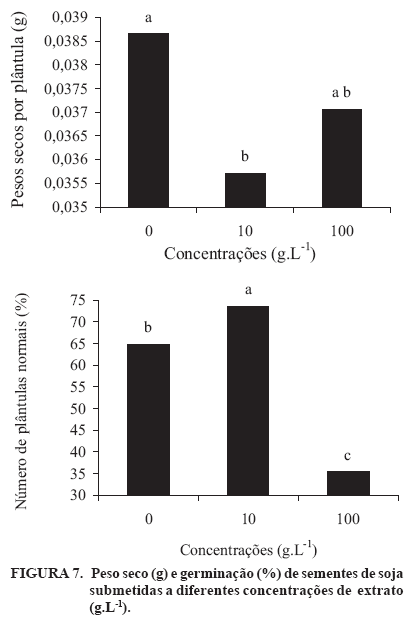
Cyperus rotundus (sedge) is a perennial plant that is difficult to control. Its subterranean organs produce inhibitors that can interfere with the germination and growth of sprouts and plants of various species, a phenomenon called allelopathy. The inhibition of seed germination may be associated with the interference of allelopathic substances in the activity of key enzymes in the germination process. The physiological quality and the activity of the enzymes involved in the germination process of corn, bean, soybean, and lettuce seeds submitted to sedge bulb extract were evaluated. The seeds were germinated in a substrate containing 10 g L-1 and 100 g L-1 concentrations of sedge bulb extract and distilled water. The physiological quality was evaluated by means of germination and vigor tests. The activities of superoxide dismutase and esterase were evaluated for all the species, catalase for corn and bean seeds, peroxidase and endo-b-mananase for lettuce seeds, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase and a-amylase for corn seed and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase for soybeans. A decrease in germination of lettuce seeds with an increase in the concentration of the extract was observed. The inhibition of corn and bean seed germination and the stimulus to germination of soybeans submitted to an extract concentration of 10 g L-1, as well as the inhibition of soybean germination in the presence of a concentration of 100 g L-1 of extract were observed. A reduction in the activities of superoxide dismutase, endo-b-mananase, peroxidase and a-amylase with an increase in the concentration of extract was detected. An increase in the activities of glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase with an increase in extract concentration was observed, indicating a loss in seed quality. A lower esterase activity was found in lettuce seeds submitted to substrate containing an extract concentration of 100 g L-1, while a lower activity of this enzyme was observed in soybeans at concentrations of 0 and 100 g L-1. Differentiated patterns were observed for catalase in corn seeds at 10 and 100 g L-1 extract concentrations. The results indicated that sedge extract contains physiological quality interferes with germination and seed-enzyme activities of corn, bean, soybean and lettuce seeds.
Cyperus rotundus; allelopathy; seeds germination