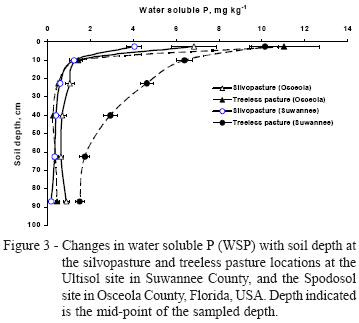
We hypothesized that, because of the ability of trees to sequester carbon (C) in the deep soil profile and remove excess nutrients from soils, the silvopastoral agroforestry system could enhance the environmental quality of the agricultural lands. To test this hypothesis, two sets of experiments were conducted in two soil orders in Florida, Spodosols and Ultisols, with two major objectives: i) determining the soil C accumulation and tracing the plant sources of C in soil fractions, and ii) quantifying water soluble phosphorus (WSP) and estimating the Soil P Storage Capacity (SPSC). Total C in both soil orders was greater under silvopasture than in treeless pastures, particularly at lower depths. Stable-isotope signature analysis suggested that C3 plants (in this case, slash pine, Pinus elliotii) contributed to a more stable C fraction than C4 plants (in this case, bahiagrass, Paspalum notatum) at soil depths up to 1 m. WSP was consistently higher in treeless pastures, while the remaining SPSC was lower in this land-use system, suggesting the greater likelihood of P moving out of the soil under treeless pasture than in silvopasture. Thus, the presence of trees in pastures contributed to more stable C within the soil profiles, lower WSP, and greater SPSC, indicating more environmental benefits provided by silvopastoral systems as compared to treeless pastures under similar ecological settings.
carbon sequestration; nutrients; soil P storage capacity; treeless pasture