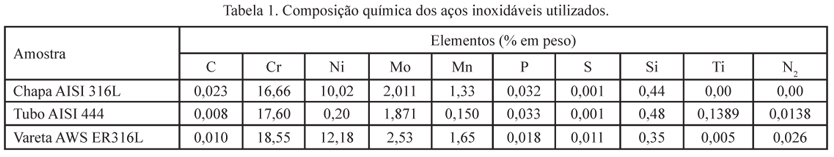
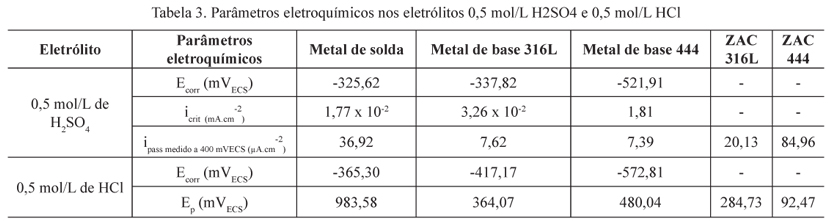
The AISI 444 stainless steel (SS) has become an option to substitute the AISI 316L SS because its low cost and satisfactory corrosion resistance. However, the use of AISI 444 alloy tubes in heat exchangers cause the welding of a dissimilar joint. The aim of this study was evaluate the corrosion resistance of the tube-to-tubesheet welded by TIG process composed of AISI 316L and AISI 444. Preparation of samples was executed through replication of tube-to-tubesheet joints. In order to test the corrosion resistance of welded joint the following tests were applied, sensitization, mass loss from room temperature up to 90 ºC, and electrochemical corrosion tests in 0,5 mol/L HCl and 0,5 mol/L H2SO4 electrolytes. The results have shown that the dissimilar joint suffers galvanic corrosion with increased degradation of the heat affected zone (HAZ) of the AISI 444 tube. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of localized corrosion (pit and intergranular) was more active in the AISI 316L alloy. It is concluded that the dissimilar joint showed better corrosion resistance than the welded joint composed solely by AISI 316L at temperatures up to 70 ºC, as the conditions observed in this work.
Corrosion; AISI 316L; AISI 444; GTAW welding; tube-to-tubesheet