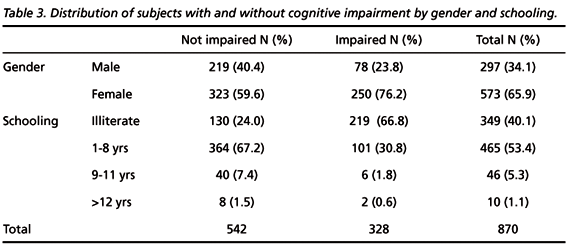
The study aims to evaluate the prevalence of cognitive/functional impairment in community-dwelling elderly above 60 years of age (n= 870; m=297, f=573) and the relationship of age, gender, and functional impairment with cognitive impairment using Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Pfeffer Functional Activities Questionnaire (PFAQ). Chi-square and Student's tests were used to compare cognitive and functional deficits. Linear regression assessed MMSE/PFAQ relationship. Stratified analysis assessed confounding factors. Logistic regression assessed the relationship among age/gender/functional status with cognitive impairment (p<0.05). Prevalence of cognitive/functional impairment was 19.2%. Functional and cognitive impairment are negatively correlated (Pearson= 0.737), despite educational level (illiterate/literate: OR=15.60; p=0/OR = 16.40; p=0). Age and gender (female) were associated with cognitive/functional impairment. Functional impairment is highly correlated to cognitive impairment. Family/health professionals may recognize functional impairment more easily than cognitive impairment. Thus, the use in combination of cognitive and functional scales is important when screening for dementia.
functional status; cognitive impairment; epidemiology; prevalence; risk factors